As trivial as it sounds, diarrhea can be classified as a dangerous disease
For Indonesian people, diarrhea is a common disease. But did you know that diarrhea can become a malignant disease?
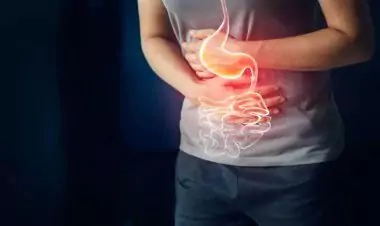
Our ears are already familiar with this disease. Diarrhea is a common thing that often occurs in various age groups, both adults and even babies. Several factors can cause diarrhea. However, diarrhea can actually be a dangerous disease.
Understanding Diarrhea
Diarrhea is a condition when a person defecates more often than usual. A person can be categorized as having diarrhea if they defecate three or more times a day. Apart from that, the dirt excreted is also thinner and can even be liquid.
There are two types of diarrhea that often occur, namely acute and chronic. Acute diarrhea is diarrhea that lasts for a short time. This type of diarrhea is a common health problem. Acute diarrhea usually lasts about one to two days but can also take longer. Then acute diarrhea usually goes away on its own.
Diarrhea that lasts more than a week is a sign of a more serious problem. Diarrhea that lasts for at least four weeks can be a symptom of chronic disease. The initial symptoms of chronic diarrhea are continuous or come and go.
Risk Factors for Acute Diarrhea and Chronic Diarrhea
There are several factors that can increase a person's risk of developing acute diarrhea or chronic diarrhea, including:
- Rarely wash your hands after going to the toilet
- Food storage and places/containers that are not clean
- Rarely cleans the kitchen and toilet area
- Water sources that are not clean
- Eating cold leftover food
- Do not wash your hands with special hand-washing soap
The points above are several general factors that can cause acute diarrhea or chronic diarrhea.
Causes of Diarrhea
There are several conditions that can cause someone to experience diarrhea. In general, diarrhea is caused by the following things:
- Bacteria in the food or water consumed.
- Viruses such as flu, rotavirus, or norovirus. Norovirus is one of the most common causes of acute diarrhea in children.
- Parasites are small organisms that are often found in contaminated food or drinking water.
- Intolerance or sensitivity to foods such as fructose and lactose.
- Allergy to a food
- Side effects of certain drugs such as antibiotics, cancer drugs, and antacids that contain magnesium.
- Diseases that affect the stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, such as Crohn's disease.
- Functional problems in the digestive organs, such as irritable bowel syndrome.
- Celiac disease is a disease that causes the body to reject gluten protein.
In some cases, a person can experience diarrhea after having surgery on the stomach. Sometimes, surgery can cause food to move through the digestive system more quickly than before.
Diarrhea Symptoms
Some symptoms of diarrhea that are usually a sign of the arrival of this disease include:
- The stool has a soft or even liquid texture.
- Pain in the stomach.
- Cramps in the stomach.
- Nausea and even vomiting.
- Pain in the head.
- Loss of appetite.
- Blood in the feces that comes out.
Dehydration can also be one of the most common symptoms accompanying diarrhea. In young children, diarrhea can be characterized by frequent urination, crying without tears, and a dry mouth.
In conditions of severe dehydration, small children may appear drowsy and unresponsive, have sunken eyes, and have pinched stomach skin that does not return quickly. Meanwhile, signs that an adult is dehydrated include fatigue, lack of energy, loss of appetite, dizziness, dry mouth, and headaches.
Diarrhea Diagnosis
The doctor will diagnose diarrhea by conducting a brief interview, physical examination, and supporting examinations, such as:
Examination of stool samples in the laboratory to identify the infection that is affecting the sufferer.
Blood tests to find out the cause of diarrhea.
Additional examinations such as sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy are necessary if there is suspicion of a more serious disease.
Complications Caused by Diarrhea
Some complications that can be caused by diarrhea include:
- Mild to severe dehydration.
- The skin around the anus area becomes irritated due to the acidic pH of the stool.
- Sepsis, or a serious infection that can spread to other organs.
- Electrolyte imbalance because electrolytes are wasted with the water that comes out during diarrhea. It can be characterized by weakness, paralysis, and even convulsions.
- Malnutrition, especially in young children less than five years old. This can result in a decrease in the immune system.
Diarrhea Treatment
There are several options you can do if you have diarrhea, including:
- Consume lots of fluids to replace fluid losses, either orally or intravenously.
- Administering drugs that can fight bacterial infections in the body.
Apart from the method in the previous point, there are several other treatments. Treatment for this disease is usually adjusted to the cause.
Prevention of Diarrhea
Several efforts can be taken to prevent diarrhea, including:
Wash your hands regularly, especially after eating, from the bathroom, after touching uncooked meat, cleaning, coughing, and so on.
Consume food and drinks that have been processed until they are perfectly cooked. So it is guaranteed to be clean.

 Leciaalvy
Leciaalvy 